Valve Flow Coefficient Cv, Kv, Av
Flow Coefficient Cv
The flow coefficient Cv states the flow capacity of a valve in gal (U.S.)/min of water at a temperature of 60℉ that will flow through a valve with a pressure loss of one pound per square inch at a specific opening position, as defined by the equation:

Where
Q = U.S. gal/min
Δp0 = reference differential pressure = 1 lb/in.2
Δp = operating differential pressure in lb/in.2
ρ0 = density of reference fluid, water = 62.4 lb/ft3
ρ = density of operating fluid in lb/ft3
Because ρ/ρ0 = specific gravity and the numerical value of Δp0 is unity,
Equation 2-12 is normally presented in the form:

Where
G = specific gravity
This relationship is incorporated in the International Standards Associ- ation (ISA) standards S.39.1 to S.39.4 and Publication 534- 119 of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), and applies to single- phase and fully turbulent flow of Newtonian liquids. For other flow conditions, refer to the above ISA standards, IEC Publication 534-2 Parts 1 and 2, or Reference 20.
Flow Coefficient Kv
The flow coefficient Kv is a version of coefficient Cv in mixed SI units. It states the number of cubic meters per hour of water at a tem- perature between 5◦ and 40◦ C that will flow through the valve with a pressure loss of one bar at a specific opening position, as defined by the equation:

here
Q = m3/hour
Δp0 = reference differential pressure = 1 bar
Δp = operating differential pressure, bar
ρ0 = density of reference fluid (water = 1, 000 kg/m3 )
ρ = density of operating fluid, kg/m3
Because ρ/ρ0 = specific gravity and the numerical value of Δp0 is unity, Equation 2-14 is normally presented in the form:

where
G = specific gravity
This relationship is contained in the IEC Publication 534- 119 and applies to single-phase and fully turbulent flow of Newtonian liquids. For other flow conditions, refer to IEC Publication 534-2, Parts 1 and 2, or to manufacturer’s catalogs.
Flow Coefficient Av
The flow coefficient Av is a version of the flow coefficient Kv incoherent SI units. Av states the number of cubic meters per second of water at a temperature between 5。and 40 。C that will flow through the valve with a pressure loss of one Pascal at a specific opening position, as defined by the equation:

where
Q = flow rate, m3/s
p = operational differential pressure, Pa
ρ = density of Newtonian liquid, kg/m3
Av is derived from Equation 2-8, which maybe presented in the following forms:

v = flow velocity of fluid, m/s
A = cross-sectional area, m2
The expression 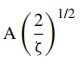 is replaced in Equation 2-16 by a single expression Av .
is replaced in Equation 2-16 by a single expression Av .
This relationship is contained in IEC Publication 534- 119 and applies to single-phase and fully turbulent flow of Newtonian liquids. For other flow condition, see IEC Publication 534-2, Parts 1 and 2.





